Yellowstone, a jewel of US tourism, is more than just a national park; it’s a living geological marvel, situated atop the magnificent Wyoming volcanic region. This area holds secrets of Earth’s inner power, manifested in spectacular geysers, vibrant hot springs, and majestic canyons. Exploring Yellowstone is not just about admiring scenic beauty, but also a journey to deeply understand the unique volcanic geology of this region.
Yellowstone – A National Park on a Giant Volcano Caldera
Recognized by UNESCO as a World Heritage Site, Yellowstone is famous for its pristine natural beauty and diverse terrain. However, few realize that beneath this beauty lies a dormant supervolcano, one of the largest volcanic systems on Earth. Yellowstone National Park is actually located within a volcanic depression, known as the Yellowstone Caldera, formed by colossal volcanic eruptions in the past.
The formation of the Yellowstone caldera began millions of years ago, through three major supervolcanic eruptions. The most recent eruption, about 640,000 years ago, created the current caldera and spewed out an immense amount of ash, altering global landscapes and climate. Today, traces of volcanic activity are still present throughout the park, creating a priceless natural geological laboratory.
Discovering Unique Geothermal Phenomena
Yellowstone’s volcanic geology is the origin of countless fascinating geothermal phenomena, making it one of the most geothermally active areas in the world. The park boasts over 10,000 hot springs, mud pots, and geysers, accounting for more than half of all geothermal features globally.
Geysers – Symbols of Geothermal Power
Geysers are among Yellowstone’s most captivating attractions. Groundwater seeps deep into the earth, comes into contact with hot rocks heated by volcanic magma, and is heated to boiling point. Accumulated steam pressure causes hot water and steam to erupt forcefully above the surface, creating spectacular towering water columns.
Old Faithful, Yellowstone’s most famous geyser, erupts regularly at predictable intervals, becoming an icon of the park. However, Yellowstone is also home to many other geysers with diverse sizes and eruption styles, such as Steamboat Geyser, the world’s tallest active geyser, or Grand Geyser, with its prolonged and complex eruptions.
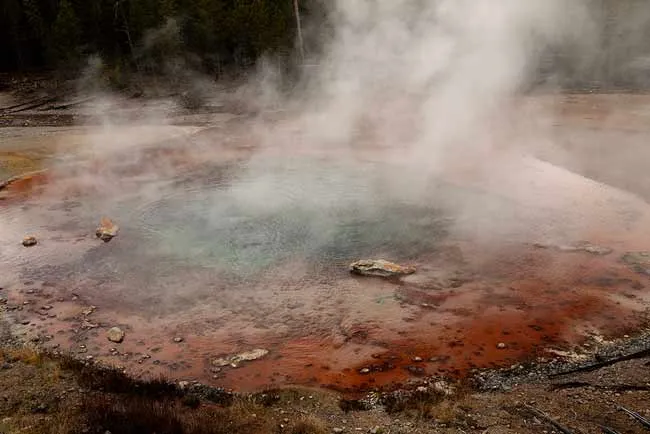

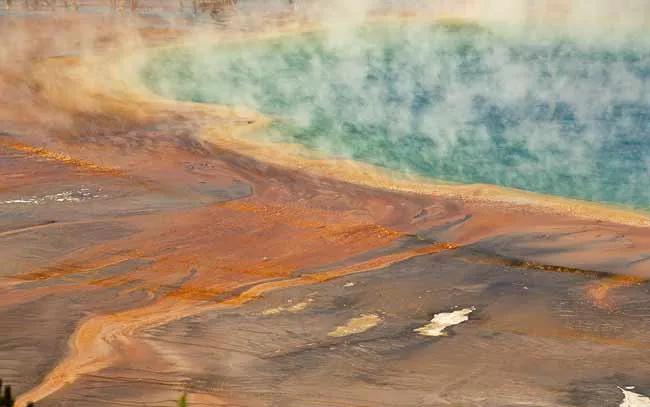
Hot Springs and Mud Pots – Nature’s Colorful Palette
Hot springs and mud pots in Yellowstone are also unique geological wonders. Hot water from the earth’s depths dissolves minerals, creating vibrant colors in the hot springs, ranging from sapphire blue, green, yellow, orange to red. Grand Prismatic Spring, Yellowstone’s largest hot spring, famous for its stunning rainbow-colored rings, is a prime example of the magical beauty of geothermal phenomena.
Mud pots are another form of geothermal feature, where steam and volcanic gases escape through liquid mud, creating bubbling and steaming mud pools. The characteristic sulfur smell in mud pot areas is a sign of underground volcanic activity. Sulphur Caldron is a typical example of a vibrant and colorful mud pot in Yellowstone.

Yellowstone’s Diverse Geology and Landscape
Volcanic geology not only creates geothermal features but also shapes Yellowstone’s unique landscape. The Grand Canyon of the Yellowstone, with its golden cliffs and magnificent waterfalls, was formed by the erosion of the Yellowstone River on volcanic rock. The canyon’s distinctive yellow color is due to the alteration of the rock under the influence of heat and hot water from the earth.
Mammoth Hot Springs, with its white travertine terraces, is the result of mineral-rich hot water flowing over the surface and depositing calcium carbonate. This unique terrace structure is constantly changing due to geothermal activity and mineral deposition.

Guide to Exploring Yellowstone’s Geology
To delve deeper into the geology of the Yellowstone volcanic region, visitors can explore the following locations:
- Canyon Village Visitor Education Center: This center provides detailed information about Yellowstone’s geology, volcanic history, and ecosystems through interactive exhibits and documentary films.
- Norris Geyser Basin: The oldest and hottest geothermal area in Yellowstone, with a variety of geysers, hot springs, and mud pots. Boardwalk trails allow visitors to explore geothermal features up close.
- Upper Geyser Basin: Home to Old Faithful Geyser and many other major geysers. Observation Point provides panoramic views of the area.
- Mammoth Hot Springs: Explore the unique travertine terraces by walking on boardwalks or driving the Upper Terrace Drive.
- Grand Canyon of the Yellowstone: Admire the canyon from various viewpoints on the North and South Rims, learn about the canyon’s formation by the Yellowstone River and geothermal activity.
Additionally, participating in Ranger Programs organized by park rangers is an excellent way to learn about Yellowstone’s geology from experts. These programs often include talks, guided walks, and interactive activities.
Conclusion
Yellowstone is not only a national park with stunning natural landscapes but also a unique outdoor geological museum. Exploring the geology of the Wyoming volcanic region at Yellowstone offers visitors invaluable educational and discovery experiences, helping us better understand the extraordinary power of Earth and the geological processes that have shaped our planet. Come to Yellowstone to admire its majestic beauty and discover the geological secrets hidden beneath the surface!