Alaska, the land of wonders, is not only famous for its majestic mountains, magnificent glaciers, and magical aurora borealis. It also harbors another invaluable natural treasure: a vast and diverse forest ecosystem. Alaskan forests are not only the green lungs of the planet but also home to countless rare species of flora and fauna, holding fascinating and mysterious stories yet to be fully discovered.
This article will take you on a journey to explore the fascinating aspects of Alaska’s forest ecosystem, from the immense taiga forests to the unique coastal temperate rainforests, to better understand the unspoiled beauty and importance of this “green lung” for the natural world.
Overview of Alaska’s Forest Ecosystem
Alaska boasts a massive forest area, accounting for about 1/3 of the state’s landmass, equivalent to the size of Germany. The forest ecosystem here is incredibly diverse, divided into various types depending on geographical location, climate, and elevation. However, the two main and most important forest types in Alaska are taiga forests (boreal coniferous forests) and coastal temperate rainforests.
Taiga forests, also known as boreal forests, cover most of inland Alaska. This is one of the largest terrestrial biomes in the world, playing a crucial role in global climate regulation and carbon storage. The Alaskan taiga is characterized by coniferous trees such as spruce, pine, and fir, along with shrubs and lichens.
Coastal temperate rainforests in Alaska, in contrast, are smaller in area but incredibly unique and biodiverse. This type of forest thrives along the southern and southeastern coasts of Alaska, where there is high rainfall and a milder climate. Alaskan temperate rainforests are famous for giant old-growth trees such as Sitka spruce, hemlock, and western redcedar, along with rich and diverse undergrowth.
Amazing Biodiversity in Alaska’s Forests
Alaska’s forest ecosystem is home to countless species of flora and fauna, from familiar large mammals to tiny insects and rare fungi. This biodiversity is the result of a combination of geographical factors, climate, and the unique evolutionary history of the region.
In the taiga forest, typical animal species include Alaskan brown bears, moose, caribou, wolves, red foxes, river otters, and many bird species such as bald eagles, snowy owls, woodpeckers, and sparrows. Taiga forests are also habitats for many freshwater fish in rivers and lakes, such as salmon, trout, and pike.
Coastal temperate rainforests in Alaska have even higher biodiversity. They not only host terrestrial animals similar to the taiga but also many species characteristic of coastal and island regions, such as American black bears, Sitka black-tailed deer, sea otters, seals, sea lions, and whales. Temperate rainforests are also habitats for many rare seabirds and migratory birds.
In terms of flora, Alaska’s forests are also incredibly rich. Taiga forests are mainly composed of coniferous trees such as white spruce, black spruce, lodgepole pine, and balsam fir. Under the forest canopy, there are shrubs such as blueberry, raspberry, and lichens. Coastal temperate rainforests have even greater plant diversity, with tree species such as Sitka spruce, hemlock, western redcedar, along with ferns, mosses, lichens, and many other herbaceous plants.
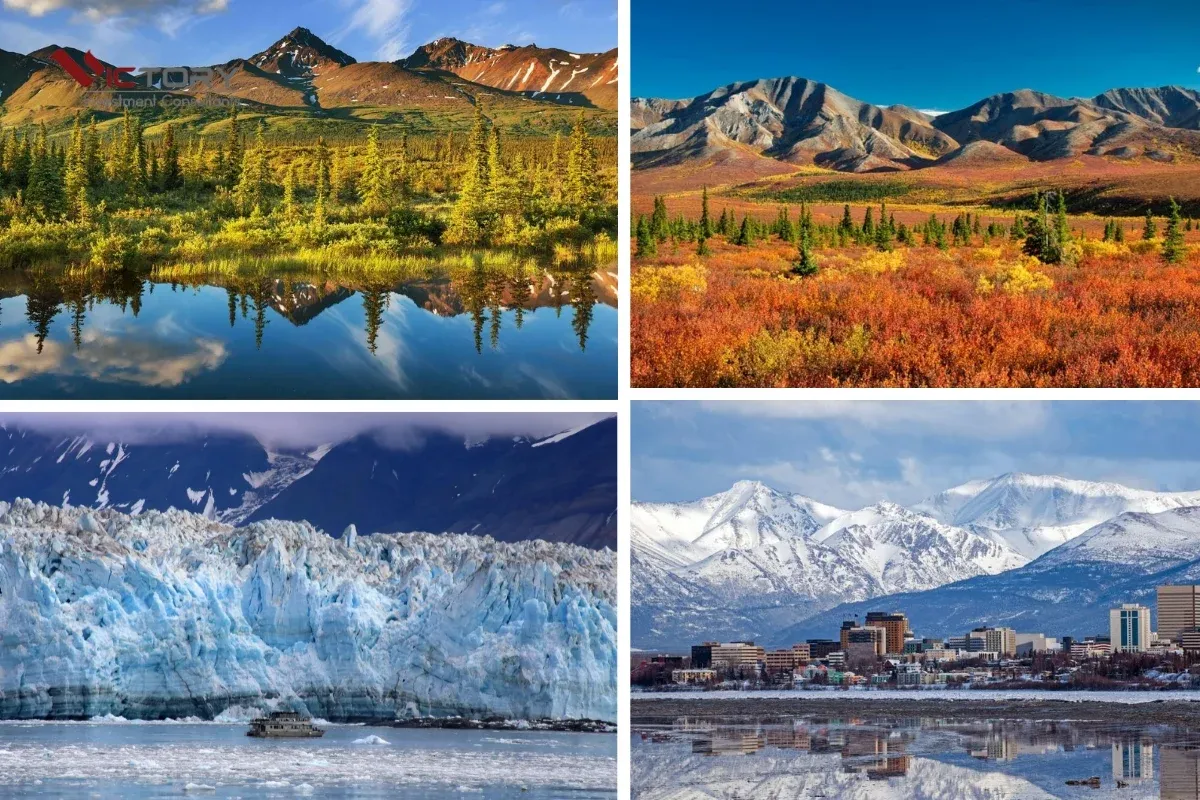

Notable Features of the Alaskan Taiga
The Alaskan taiga has unique characteristics, reflecting the adaptation of organisms to the harsh climate of the subarctic region. One of the most prominent features of the taiga is the dominance of coniferous tree species, which are well-adapted to cold and drought conditions. Small needles and thick bark help trees minimize water loss and withstand heavy snow cover.
The soil in the taiga forest is often nutrient-poor and permafrost (permanently frozen ground) is present in some areas. Permafrost is a year-round frozen soil layer, significantly affecting plant growth and the ecosystem. Trees in the taiga forest must adapt to live on the thin layer of soil above the permafrost, with shallow root systems and good waterlogging tolerance.
The Alaskan taiga plays an important role in the global carbon cycle. Taiga forests store a large amount of carbon in plant biomass and permafrost soil. However, climate change is melting permafrost, potentially releasing large amounts of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, causing serious consequences for the global climate.

The Wonderful Beauty of Alaska’s Coastal Temperate Rainforests
Alaska’s coastal temperate rainforests are a unique and rare ecosystem, only existing in a few coastal regions with mild climates and high rainfall around the world. Alaskan temperate rainforests are famous for their unspoiled, majestic beauty and high biodiversity.
Giant old-growth trees in Alaska’s temperate rainforests, such as Sitka spruce, hemlock, and western redcedar, can live for hundreds, even thousands of years and reach heights of dozens of meters. Beneath the dense forest canopy is a rich plant world with ferns, mosses, lichens, and wildflowers.
Coastal temperate rainforests in Alaska are also ideal habitats for many rare animal species, especially those dependent on old-growth forests and abundant freshwater sources. Streams and rivers in the forest are spawning grounds for salmon, an important food source for bears, eagles, and other animals.

Importance of Alaska’s Forest Ecosystem
Alaska’s forest ecosystem is of immense importance not only to Alaska but also to the entire world. Ecologically, Alaskan forests play a vital role in climate regulation, water resource protection, biodiversity maintenance, and providing habitats for many species of flora and fauna. Alaskan forests are also a source of timber and important forest products, contributing to the local and national economy.
Culturally, Alaskan forests have special significance for indigenous communities, who have lived in and been connected to the forests for thousands of years. Forests provide food, building materials, medicine, and are an integral part of their culture and spirit.
In addition, Alaskan forests are an attractive tourist destination, attracting visitors from around the world to explore the unspoiled beauty and experience outdoor activities such as hiking, camping, fishing, kayaking, and wildlife viewing. Ecotourism based on forests has sustainable development potential, bringing economic benefits to local communities and raising awareness of forest conservation.
Conserving Alaska’s Forest Ecosystem
Alaska’s forest ecosystem faces many challenges, including climate change, over-logging, wildfires, and other economic development activities. Climate change is causing negative impacts on Alaskan forests, such as increasing temperatures, changing rainfall patterns, causing prolonged heat waves and droughts, increasing the risk of wildfires and forest pests.
To conserve Alaska’s forest ecosystem, close coordination is needed between the government, conservation organizations, local communities, and citizens. Conservation measures should focus on sustainable forest management, mitigating the impacts of climate change, preventing wildfires, protecting biodiversity, and developing responsible ecotourism.
Conserving Alaskan forests is not only the responsibility of Alaskans but also the shared responsibility of all humanity. Because Alaskan forests are an important part of the global ecosystem, contributing to the balance of the planet and bringing invaluable benefits to us all.
Conclusion
Alaska’s forest ecosystem is an invaluable natural treasure, harboring unspoiled, wonderful beauty and rich biodiversity. From the vast taiga forests to the unique coastal temperate rainforests, each forest type carries its own unique characteristics and plays an important role in the global ecosystem.
Exploring and learning about Alaska’s forest ecosystem not only helps us expand our knowledge of the natural world but also raises awareness of conservation and environmental protection responsibility. Let’s join hands to take action to protect the “green lungs” of the planet, so that future generations still have the opportunity to admire the beauty and benefit from the values that Alaskan forests bring.